Here in this article we will discuss about latest cPanel & WHM Version 11.50 feature and prerequisites and installation on fresh CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 Version.
Latest Features of cPanel & WHM 11.50 :
CentOS , CloudLinux , and RHEL 7 support
Use the XFS or ext4 filesystems.
Less booting time
Greylisting feature : which protect server from unwanted emails and untrusted email servers .
Installation Recommended settings:
Disable OS Firewall before installation .
Recommended Hardware :
Minimum & Recommended Processor should be 226MHZ
Minimum RAM should be 1 GB.
Minimum Disk Space should be 20 GB .
Installation of cPanel in CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 / CloudLinux 7 :
Before doing cpanel & WHM installation first ensure your OS Version , RAM and diskspace.
Deactivate firewall on CentOS 7 , CloudLinux 7 and RHEL 7 :
# iptables-save > ~/iptables.rules
# systemctl stop firewalld.service
# systemctl disable firewalld.service
Disable Security Enhanced Features ( SELinux ) :
If your server running SELinux Features of security, then disable this features .
To disable , run the below command.
Edit the configuration file /etc/selinux/config and set the parameter SELINUX to disabled, below is my configuration file , after set the parameter you need to reboot the server.
# vim /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=permissive
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
Installation set up steps :
cPanel installation need perl package , so we need to install perl before instaalation .
After installation of perl, set the hostname of server , the hostname should be in FQDN i.e fully qualified domain name. Below is steps to set hostname in Centos / RHEL 7.
Below command to check hostname of server :
To set hostname :
#hostnamectl set-hostname cpanel.techtransit.org
Install cPanel/WHM
Now we will download cpanel script on home directory of server , which will install cpanel & WHM .Follow below steps for installation.
# cd /home
# curl -o latest -L https://securedownloads.cpanel.net/latest
# sh latest
Now script will run some hours and after installation you will get some output like , time taken in installation as well as server access url and access details, you will use in login root as a user and use password of root user.
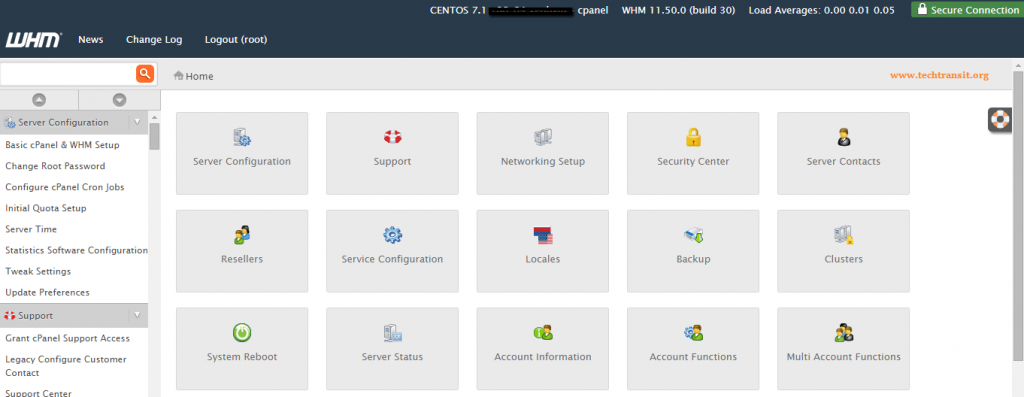
You will get WHM access like below url.
ACCESS URL:
https://your –server-public-ip:2087/
OR
https://server-hostname:2087/
cpanel_11.50_centos7
After access of url in browser and put the username password details in access url and accept license agreement, you can configure server networking, ip address and nameserver as according to you , you should have good nice knowledge of System Admin part.
Hope you enjoy this post , for any concern please comment here and give us feedback. Thanks