Installing DHCP role via new Server Manager
Ensure the computer has at least one static IP address assigned before starting the role installation.
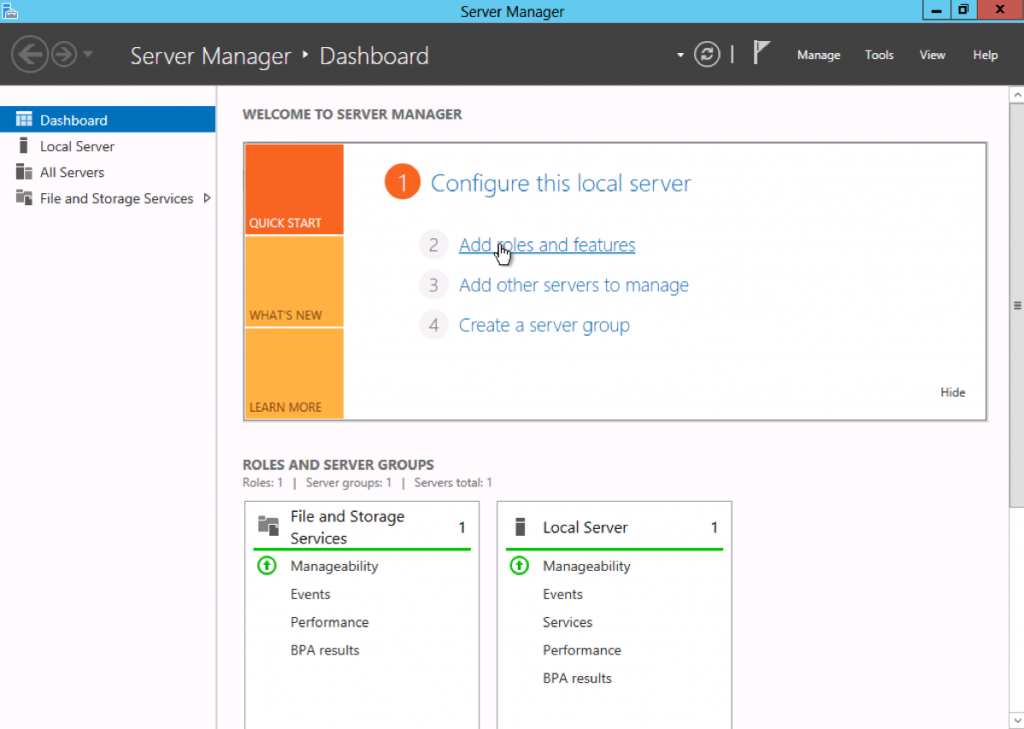
Launch the Add Role Wizard from Server Manager.
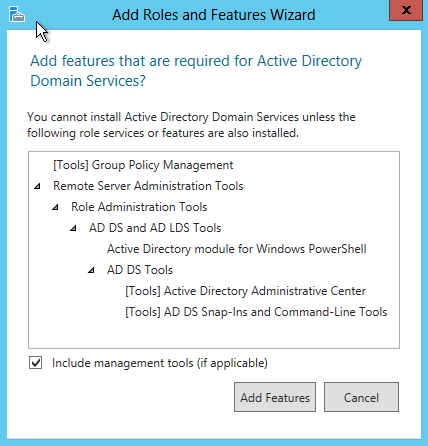
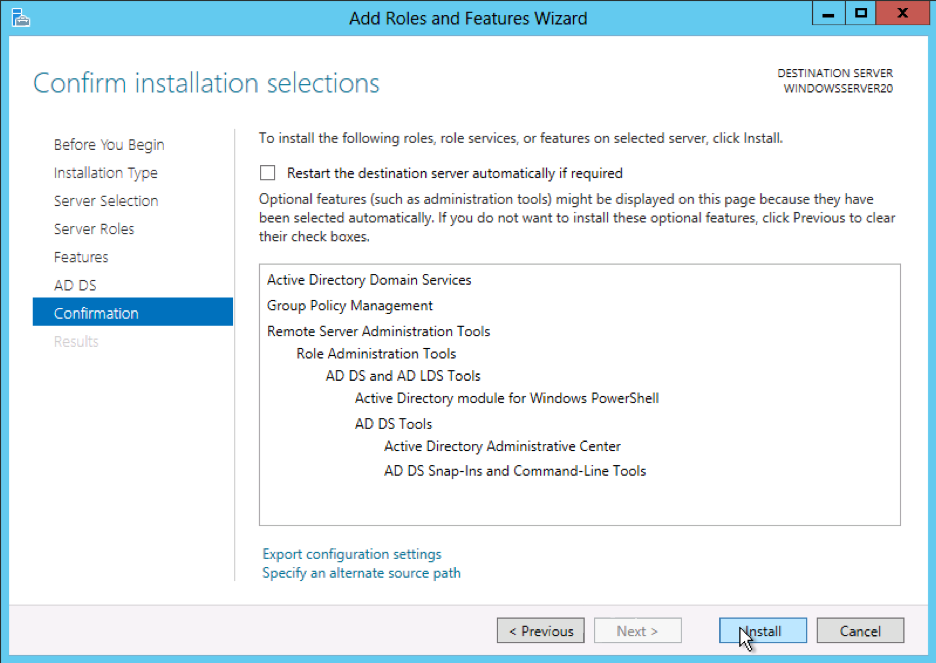
Select DHCP server role and go through the steps needed for installation.
The last page of the wizard (which comes up after the role has been installed), provides a link – “Complete DHCP configuration”.
This provides some tasks that need to be performed to enable the DHCP server role to work properly after role installation.

Launch the DHCP post-install wizard and complete the steps required.
Creation of DHCP security groups (DHCP Administrators and DHCP Users). For these security groups to be effective, the DHCP server service needs to be restarted. This will need to be performed separately by the administrator.

Authorization of DHCP server in Active Directory (only in case of a domain-joint setup). In a domain joined environment, only after the DHCP server is authorized, it will start serving the DHCP client requests. Authorization of DHCP server can only be performed by a domain user that has permissions to create objects in the Net services container in Active Directory. See how to delegate permissions to do this in active directory.

Figure 3: DHCP Post-Install configuration wizard – Authorization Page

In case completing of the post-install step is missed after role installation, the administrator will continue to see a notification on the action pane and also a link on the DHCP role tile on the main Server Manager page suggesting that some configuration is required. That link would go away only after completion of the post-install task.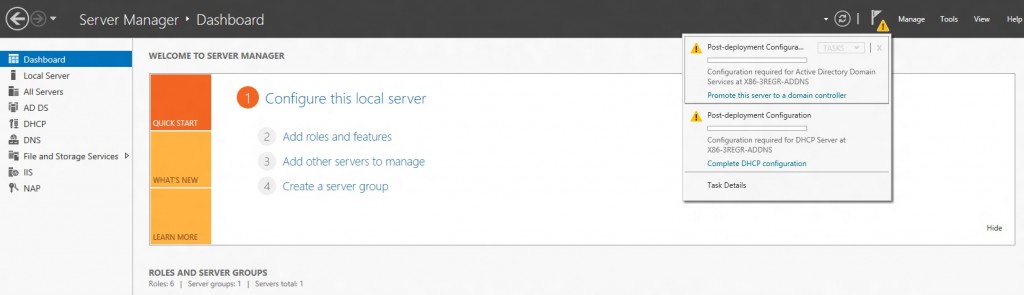
The configuration of DHCP server parameters such as scope, options etc. are no longer available in the new Server Manager. The administrator can now launch DHCP MMC either via Server manager (as shown below), or via the DHCP MMC application in the Start Menu, or writing dhcpmgmt.msc on the command prompt. The administrator can now create scopes, set option values so as to be able to lease out IP addresses and provide option values to clients.

Installing via PowerShell
To install the DHCP server role via PowerShell, one needs to run the following command:
Command: Add-WindowsFeature -IncludeManagementTools dhcp
Note the extra switch (IncludeManagementTools) which is now needed, in contrast to Windows 7. Without this switch, just the DHCP server role would be installed. The DHCP server RSAT tools which includes DHCP MMC, netsh context and the new DHCP PowerShell cmdlets, is not installed by default, unless you give the above flag.
After the role is installed, there are a few other steps that the administrator needs to perform so that the server can work correctly and lease out addresses. This the post-install configuration as performed by the above mentioned post-install wizard. The administrator can either launch the Server Manager and complete the DHCP post-installation task from there (as this is UI-only task) or run the below set of commands which are an equivalent of above.
Creating DHCP security groups
Creating DHCP security groups
Command:netsh dhcp add securitygroups
You will need to restart the DHCP service for these groups to become active.
Command: Restart-service dhcpserver
Authorizing the DHCP server in Active Directory (only needed for a domain-joined setup)
Command: Add-DhcpServerInDC <hostname of the DHCP server> <IP address of the DHCP server>
Now the administrator can launch DHCP MMC either via Server manager, or via the DHCP MMC application from the start menu, or by writing dhcpmgmt.msc on the command prompt. The administrator can now also create scopes, set option values so as to be able to lease out IP addresses and provide option values to clients using DHCP MMC or the new DHCP PowerShell.
If the administrator has completed the post-install configuration using PowerShell, Server Manager may still raise a flag (alert) for its completion using the post-install configuration wizard. This alert can be suppressed by notifying the Server Manager that the post-install configuration has been completed. This can be done by the below command:
Command: Set-ItemProperty –Path registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\ServerManager\Roles\12 –Name ConfigurationState –Value 2.